Complete CPA job description guide for Indian professionals covering roles, responsibilities, salary expectations, Big 4 opportunities, and career paths across experience levels.
Table of Contents
The demand for US CPA qualified professionals in India has reached unprecedented levels as multinational corporations expand their finance operations, Big 4 firms scale their service delivery centers, and Indian companies increasingly adopt global accounting standards.
If you are considering the CPA credential, understanding exactly what CPAs do on a daily basis, what employers expect from them, and how these roles translate to the Indian job market becomes essential for informed career planning.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about CPA job descriptions from an Indian professional’s perspective.
We will examine the core responsibilities that define the CPA role, break down the various practice areas from tax to audit to advisory, analyze salary expectations across experience levels, and identify the specific employers actively recruiting CPAs in India. Whether you are evaluating if CPA is the right investment for your career or preparing for job interviews after passing your exams, this guide provides the practical insights you need.
This guide is specifically designed for Indian B.Com and M.Com graduates exploring international credentials, Chartered Accountants considering CPA as a complementary qualification, and working finance professionals seeking to understand how US CPA certification can transform their career trajectory.
By the end, you will have a clear picture of what it means to work as a CPA and whether this path aligns with your professional aspirations.
What Does a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Do?
The Certified Public Accountant designation represents the highest standard of competence in the accounting profession, recognized globally for its rigorous examination process and ethical requirements. CPAs serve as trusted financial advisors to businesses, governments, nonprofits, and individuals, ensuring accuracy in financial reporting, compliance with regulations, and strategic guidance for financial decision-making. Their work touches virtually every aspect of organizational finance, from routine bookkeeping oversight to complex merger transactions.
Understanding what CPAs actually do requires looking beyond the general “accountant” label to examine the specific responsibilities that define this profession. While the exact duties vary based on employer, specialization, and seniority level, certain core functions remain consistent across most CPA roles.
What are the core job responsibilities of a CPA?
Every CPA, regardless of their specific practice area or employer type, performs certain fundamental functions that form the backbone of the profession. These core responsibilities reflect the AICPA’s professional standards and the competencies tested in the CPA examination. Mastering these areas provides the foundation upon which specialized expertise is built.
Financial Statement Preparation and Analysis
CPAs prepare, review, and analyze financial statements that organizations use for internal decision-making and external reporting to investors, regulators, and other stakeholders. This includes balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements, and statements of shareholders’ equity prepared in accordance with US GAAP or IFRS standards. The CPA ensures that these statements accurately represent the organization’s financial position and comply with all applicable accounting standards.
Audit and Assurance Services
Auditing represents one of the most distinctive CPA functions, as only licensed CPAs can sign off on audited financial statements submitted to the Securities and Exchange Commission. CPAs examine financial records for accuracy, test internal controls, verify that transactions are properly recorded, and provide independent assurance that financial statements are free from material misstatement. This assurance function maintains trust in capital markets and protects investors from fraudulent reporting.
Tax Compliance and Advisory
CPAs help individuals and organizations fulfill their tax obligations while minimizing their tax burden through legitimate planning strategies. This includes preparing and filing federal, state, and local tax returns, identifying applicable deductions and credits, ensuring compliance with constantly evolving tax regulations, and representing clients before the IRS when issues arise. Tax work requires staying current with legislative changes and understanding how they impact different types of taxpayers.
Advanced CPA Responsibilities in Senior Roles
As CPAs gain experience and advance into senior positions, their responsibilities expand beyond technical accounting work into strategic leadership and advisory functions. These advanced responsibilities typically emerge at the manager level and become increasingly prominent in director, controller, and executive roles.
Strategic Financial Planning and Forecasting
Senior CPAs develop financial projections, create budgets, and model different business scenarios to support strategic decision-making. They analyze historical trends, assess market conditions, and provide leadership with data-driven recommendations for capital allocation, expansion initiatives, and operational improvements. This forward-looking function positions CPAs as essential partners in shaping organizational strategy rather than simply recording historical transactions.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
CPAs at senior levels oversee organizational compliance with the full spectrum of financial regulations, from SEC reporting requirements to industry-specific rules. They design and implement internal control frameworks, assess risk exposure across the organization, and ensure that policies and procedures adequately address identified risks. This responsibility has grown significantly following corporate scandals and subsequent legislation like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
Client Advisory and Business Consulting
Beyond traditional accounting functions, experienced CPAs provide strategic advice to clients on business challenges ranging from operational efficiency to growth financing to succession planning. They leverage their deep understanding of financial operations to identify opportunities for improvement and guide organizations through complex decisions. This advisory role positions CPAs as trusted business partners rather than mere compliance professionals.
What Types of Jobs Are Covered Under a CPA Job Description by Practice Area?
CPAs typically specialize in one of several practice areas, each with distinct responsibilities, required skills, and career trajectories. Understanding these specializations helps you identify which path aligns with your interests and strengths. While some CPAs maintain broader practices, most develop deep expertise in a specific area as their careers progress.
Tax CPA: Roles and Responsibilities
Tax practice represents one of the largest employment areas for CPAs, encompassing everything from individual tax return preparation to complex international tax planning for multinational corporations. Tax CPAs combine technical knowledge of tax codes with strategic thinking to help clients navigate their tax obligations efficiently.
Individual and Corporate Tax Preparation
Tax CPAs prepare federal and state income tax returns for individuals, partnerships, corporations, trusts, and estates. This involves gathering financial information from clients, applying relevant tax laws to determine taxable income and applicable credits, completing required forms accurately, and filing returns by applicable deadlines. For corporate clients, this work includes quarterly estimated tax payments and year-end compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
Tax Planning and Strategy Development
Beyond compliance work, tax CPAs proactively identify opportunities to reduce clients’ tax burden through legitimate planning strategies. This includes timing of income and deductions, entity structure optimization, retirement planning, and investment decisions with tax implications. Effective tax planning requires understanding clients’ complete financial picture and anticipating how current decisions affect future tax positions.
IRS Representation and Compliance
When clients face IRS audits, inquiries, or disputes, CPAs serve as their representatives in dealings with tax authorities. This includes responding to audit requests, negotiating settlements, filing appeals when appropriate, and ensuring clients understand their rights and obligations throughout the process. CPAs with authorization to practice before the IRS can represent clients at all administrative levels.
Audit CPA: What the Job Entails
Audit practice forms the cornerstone of the CPA profession, with auditors serving as independent evaluators of financial statement accuracy and internal control effectiveness. Audit CPAs work for public accounting firms conducting external audits or within organizations performing internal audit functions.
External Audit Responsibilities
External auditors examine client financial statements to provide independent assurance that they fairly represent the organization’s financial position in accordance with applicable accounting frameworks. This involves testing transactions, confirming balances with third parties, evaluating accounting policies, and assessing management estimates for reasonableness. The culmination of an external audit is the auditor’s opinion, which investors and creditors rely upon when making decisions.
Internal Audit Functions
Internal auditors work within organizations to evaluate and improve risk management, control processes, and governance practices. Unlike external auditors, who focus primarily on financial statement accuracy, internal auditors examine operational efficiency, compliance with policies, and the effectiveness of internal controls across all organizational functions. They report findings and recommendations to management and the audit committee.
SOX Compliance and Controls Testing
Following the Sarbanes-Oxley Act requirements for public companies, CPAs perform extensive testing of internal controls over financial reporting. This includes documenting control processes, testing control effectiveness, identifying deficiencies, and evaluating whether weaknesses rise to the level of material weaknesses requiring disclosure. SOX compliance work represents a significant portion of audit practice for firms serving public company clients.
Advisory and Consulting CPA Roles
Advisory services represent the fastest-growing practice area for CPAs, as organizations increasingly seek expert guidance on complex business challenges beyond traditional accounting and audit matters. Advisory CPAs leverage their financial expertise to help clients solve problems and capitalize on opportunities.
Management Consulting Responsibilities
Management consulting CPAs help organizations improve performance through operational analysis, process optimization, and strategic recommendations. They assess current state operations, benchmark against industry practices, identify improvement opportunities, and support implementation of recommended changes. This work spans functions from finance department effectiveness to enterprise-wide transformation initiatives.
Forensic Accounting and Fraud Investigation
Forensic accountants investigate suspected fraud, embezzlement, and financial irregularities using specialized techniques to trace funds, analyze transactions, and identify perpetrators. They work with legal counsel on litigation support, provide expert witness testimony, and help organizations recover from financial crimes. This specialty combines accounting expertise with investigative skills and legal understanding.
Mergers and Acquisitions Support
CPAs provide critical support throughout M&A transactions, from initial target identification through post-merger integration. Their responsibilities include financial due diligence to identify risks and opportunities, valuation analysis, deal structuring advice, and integration planning for finance functions. M&A advisory work requires strong analytical skills and the ability to work under tight deadlines.
Where Do CPAs Work in India?
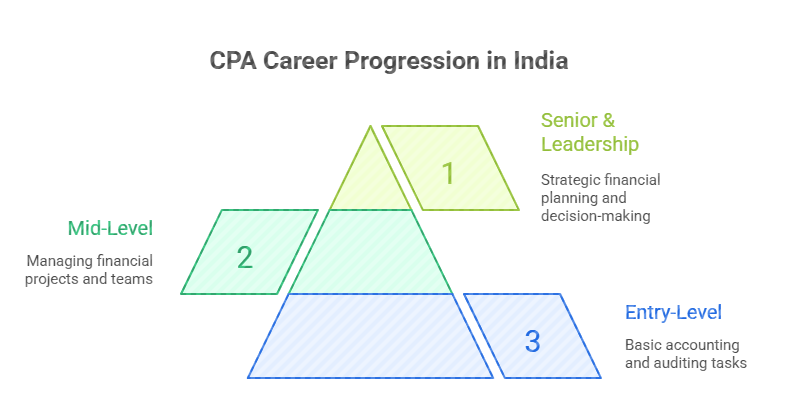
CPA career progression follows a fairly predictable path, with responsibilities and compensation increasing as professionals gain experience and demonstrate competence. Understanding what is expected at each career stage helps you set realistic expectations and prepare for advancement. The typical progression moves from entry-level positions through mid-career management roles to senior leadership.
Entry-Level CPA Job Description (0-2 Years Experience)
Entry-level CPAs focus on building foundational skills through hands-on work under supervision. These positions emphasize learning organizational processes, developing technical proficiency, and demonstrating reliability and attention to detail.
Staff Accountant Responsibilities
Staff accountants handle fundamental accounting functions including journal entries, account reconciliations, and financial statement preparation under supervision. They maintain accurate records of daily transactions, assist with month-end close processes, and prepare supporting documentation for audit requests. This role provides broad exposure to accounting operations and serves as the training ground for more specialized responsibilities.
Associate Auditor Functions
Associate auditors execute audit procedures under senior team members’ direction, including testing transactions, confirming balances, and documenting work performed. They learn audit methodology through practical application, develop professional skepticism, and begin building client relationship skills. The associate level typically involves significant client-site work and exposure to various industries.
Skills Expected at Entry Level
Employers expect entry-level CPAs to demonstrate strong technical accounting knowledge, proficiency with spreadsheets and accounting software, excellent attention to detail, and solid written and verbal communication skills. Additionally, they should show ability to work effectively in teams, meet deadlines under pressure, and maintain professional demeanor with clients and colleagues.
Mid-Level CPA Roles (3-7 Years Experience)
Mid-level CPAs assume increasing responsibility for work quality, begin supervising junior staff, and develop specialized expertise in their practice area. These positions bridge the gap between execution and management, requiring both technical excellence and emerging leadership capabilities.
Senior Accountant Job Description
Senior accountants take ownership of complete accounting cycles, identify and resolve complex issues, and ensure accuracy of financial reporting with minimal supervision. They mentor junior team members, review their work for quality, and serve as technical resources for accounting questions. Senior accountants often specialize in specific areas like revenue recognition, consolidations, or technical accounting research.
Audit Manager Responsibilities
Audit managers oversee engagement execution, ensuring work meets quality standards and deadlines while staying within budget. They manage multiple engagements simultaneously, maintain client relationships, identify additional service opportunities, and address complex accounting and auditing issues. Audit managers also handle staff scheduling, performance feedback, and professional development coaching for their teams.
Tax Manager Functions
Tax managers supervise tax compliance and planning engagements, review returns prepared by staff, and serve as the primary client contact for tax matters. They stay current with legislative changes, provide tax planning recommendations to clients, and ensure the firm’s tax work meets quality and ethical standards. Tax managers also develop staff technical capabilities and participate in practice development initiatives.
Senior and Leadership CPA Positions (8+ Years Experience)
Senior CPAs transition from technical execution to strategic leadership, focusing on business development, organizational direction, and mentoring the next generation of professionals. These roles require proven track records of delivering results and developing others.
Finance Director Responsibilities
Finance directors oversee financial operations for their organizations, ensuring accurate reporting, effective controls, and efficient processes. They manage finance teams, set departmental strategy, and partner with business leaders on financial aspects of operational decisions. Finance directors also lead special projects like system implementations, process improvements, and organizational changes.
CFO Role and Expectations
Chief Financial Officers serve as senior executives responsible for all financial functions, including accounting, treasury, tax, and investor relations. They provide strategic guidance to the CEO and board, lead capital allocation decisions, manage relationships with investors and lenders, and ensure the organization maintains financial health. CFOs also navigate regulatory requirements and represent the company in financial communications.
Partner Track in Public Accounting
Partners own equity in their firms and bear ultimate responsibility for client relationships, practice growth, and firm governance. They develop new business, maintain significant client relationships, ensure engagement quality, and mentor the next generation of firm leaders. Partners participate in firm strategy and management while continuing to deliver high-level client service in their practice areas.
CPA Job Opportunities in India: Where CPAs Work
The Indian job market for US CPAs has expanded significantly as global companies establish operations in India and Indian organizations increasingly require international accounting expertise. Understanding where CPAs find employment helps you target your job search and develop relevant skills.
Big 4 Accounting Firms in India
The Big 4 firms, including Deloitte, PwC, EY, and KPMG, represent the largest employers of CPAs in India. These firms have dramatically expanded their Indian operations, with plans to hire approximately 100,000 new employees in India in FY25 alone. Their India centers serve both domestic clients and global delivery for international engagements.
Deloitte, PwC, EY, and KPMG Job Roles
Big 4 firms in India offer CPA positions across all major service lines, including audit, tax, advisory, and consulting. Roles range from entry-level associates through senior partners, with opportunities to work on engagements for Fortune 500 clients globally. These firms particularly value CPAs for roles serving US-headquartered clients requiring US GAAP expertise and American business understanding.
Service Lines and Specializations
Within Big 4 India offices, CPAs find opportunities in external audit, internal audit, tax compliance and advisory, transaction advisory, risk consulting, technology consulting, and forensic services. Each service line offers distinct career paths with specialized skill development. The breadth of services means CPAs can often explore different areas before committing to a specialization.
Career Progression in Big 4 India
Big 4 career progression typically follows the associate, senior associate, manager, senior manager, director, and partner hierarchy. Advancement depends on performance, client relationship development, and business development contributions. The typical timeline from entry level to partner spans 12 to 15 years, though high performers may advance more quickly. India-based roles increasingly offer paths to international assignments and global leadership positions.
Multinational Corporations and Global Capability Centers
Major multinational corporations have established Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in India to handle finance operations for their worldwide businesses. These centers employ thousands of finance professionals, with US CPAs particularly valued for their expertise in American accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
Finance Shared Services Roles
Shared services centers consolidate routine finance functions like accounts payable, accounts receivable, and general accounting for organizations operating globally. CPAs in these centers perform transaction processing, account reconciliations, and financial reporting while ensuring compliance with US GAAP and internal control requirements. Career progression leads from processing roles to team leadership and center management.
US GAAP Reporting Positions
Many GCCs maintain dedicated US GAAP reporting teams responsible for preparing consolidated financial statements, quarterly SEC filings, and management reports for American parent companies. CPAs with US GAAP expertise fill these positions, applying their knowledge of American accounting standards to complex consolidation and reporting challenges. These roles often involve direct interaction with US-based corporate finance leadership.
Internal Audit and Compliance Jobs
Corporate internal audit departments in India hire CPAs for roles spanning operational audits, financial audits, and compliance testing. These positions involve evaluating controls, assessing risks, and recommending improvements across global operations. CPAs with SOX experience are particularly valued for testing internal controls over financial reporting.
Indian Companies Hiring US CPAs
Beyond multinational employers, Indian companies increasingly recognize CPA value for their expanding international operations, investor relations requirements, and desire for world-class finance functions.
IT and ITES Sector Opportunities
Indian IT giants like Infosys, Wipro, TCS, and HCL hire CPAs for finance roles supporting their substantial US revenue streams. These companies require US GAAP expertise for SEC reporting, transfer pricing, and investor communications. Finance positions in IT companies offer exposure to fast-paced environments and significant international interaction.
BFSI Industry CPA Roles
Banks, insurance companies, and financial services firms employ CPAs for roles ranging from financial reporting to risk management to regulatory compliance. The increasing globalization of Indian financial services creates demand for professionals who understand international accounting and regulatory frameworks. These positions often involve complex transactions and sophisticated financial instruments.
Manufacturing and Consulting Firms
Indian manufacturing companies with export operations and consulting firms serving international clients value CPA expertise for financial management, compliance, and client service roles. CPAs help these organizations meet international customer requirements, access global capital markets, and maintain world-class finance functions.
How Much Do CPAs Earn in India?
Understanding CPA compensation in India helps you evaluate the return on your credential investment and set realistic salary expectations at different career stages. CPA salaries vary significantly based on experience level, employer type, location, and specialization.
Entry-Level CPA Salary in India
Entry-level CPAs in India typically earn between ₹6 lakhs and ₹10 lakhs per annum when joining quality employers. Big 4 firms and major multinational corporations offer packages toward the higher end of this range, while smaller organizations and regional firms may start lower. Geographic location significantly impacts starting salaries, with Mumbai, Bangalore, and Delhi offering premium compensation.
Fresh CPAs entering Big 4 firms can expect packages between ₹8 lakhs and ₹12 lakhs, depending on their educational background, interview performance, and the specific service line. Those joining leading MNC finance shared services typically see starting salaries of ₹7 lakhs to ₹10 lakhs. The CPA credential commands a premium over non-certified accountants, with an incremental value of 15% to 30% in starting compensation.
Mid-Level and Senior CPA Compensation
Mid-level CPAs with three to seven years of experience earn between ₹12 lakhs and ₹20 lakhs per annum in quality roles. Those working with US clients or on international engagements typically command packages at the higher end. Specialists in high-demand areas like transfer pricing, transaction advisory, or technology consulting may exceed these ranges.
Senior CPAs in manager and director roles earn ₹18 lakhs to ₹35 lakhs annually, with Big 4 and major MNC leadership positions reaching ₹40 lakhs to ₹50 lakhs or more.
CFO-level positions in mid-sized companies command packages of ₹50 lakhs to ₹1 crore, while leadership roles in large multinationals can exceed these figures significantly. Compensation at senior levels increasingly includes variable components tied to performance and business results.
Factors That Impact CPA Salary in India
Several factors influence CPA compensation beyond experience level. Employer type matters significantly, with Big 4 firms and multinational corporations generally paying more than domestic companies or smaller accounting practices. Location also impacts pay, with tier-one cities offering 20% to 30% premiums over tier-two locations.
Specialization affects earning potential as well. CPAs with expertise in high-demand areas like international taxation, forensic accounting, or technology advisory typically earn more than generalists. Additional credentials also boost compensation, with professionals holding both CPA and CA qualifications commanding premium packages reflecting their dual expertise. Finally, business development contribution and leadership capabilities increasingly influence compensation as careers progress beyond technical execution.
What Skills and Competencies Are Listed in a CPA Job Description?
CPA job descriptions consistently emphasize certain technical and soft skills that employers consider essential for success. Understanding these requirements helps you assess your readiness and identify development priorities.
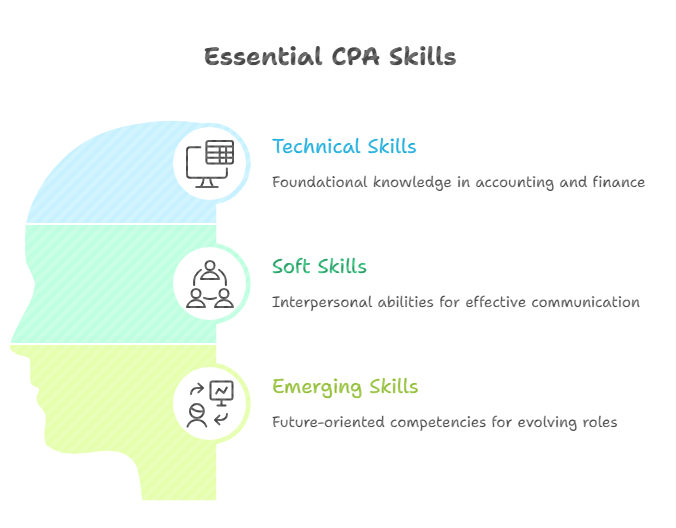
Technical Skills Every CPA Needs
Technical competence forms the foundation of CPA employment, with specific knowledge requirements varying by practice area and employer type.
US GAAP and IFRS Knowledge
CPAs must demonstrate a deep understanding of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, including revenue recognition, lease accounting, financial instruments, and consolidation requirements. For roles involving international operations, IFRS knowledge becomes equally important. The ability to apply these standards to complex transactions and research technical issues independently distinguishes strong candidates.
Tax Code and Regulatory Expertise
Tax-focused positions require comprehensive knowledge of federal and state tax codes, including individual, corporate, partnership, and estate taxation. Candidates should understand tax planning strategies, compliance requirements, and representation procedures. Staying current with legislative changes and understanding their practical implications is essential for tax practice success.
Accounting Software Proficiency
Modern CPAs must work effectively with enterprise accounting systems like SAP, Oracle, and NetSuite, along with specialized tools for their practice area. Proficiency in Excel remains essential, including advanced functions, pivot tables, and data analysis capabilities. Familiarity with audit software, tax preparation platforms, and data analytics tools increasingly appears in job requirements.
Soft Skills That Make CPAs Successful
Beyond technical competence, employers emphasize interpersonal and professional skills that enable CPAs to work effectively with clients, colleagues, and stakeholders.
Analytical Thinking and Problem Solving
CPAs must analyze complex situations, identify issues, evaluate alternatives, and develop practical solutions. This requires logical reasoning, attention to relevant details, and the ability to see patterns in large data sets. Strong analytical skills enable CPAs to move beyond routine processing to value-added advisory work.
Communication and Client Management
Effective CPAs communicate complex financial information clearly to non-technical audiences, including executives, board members, and clients. This includes written communication through reports and memos, verbal presentations, and the interpersonal skills needed to build and maintain professional relationships. Client management becomes increasingly important as careers advance.
Leadership and Team Collaboration
As CPAs progress, leadership capabilities become essential for managing teams, developing staff, and driving results. This includes delegating effectively, providing constructive feedback, motivating team members, and creating environments where people perform their best. Even at junior levels, collaboration skills and the ability to work productively in team settings matter significantly.
Emerging Skills for Future-Ready CPAs
The accounting profession continues evolving, with new skills becoming increasingly important for career success and relevance.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
CPAs increasingly work with large data sets, using analytical tools to identify trends, anomalies, and insights. Skills in data visualization, statistical analysis, and business intelligence platforms distinguish forward-thinking professionals. Understanding how to leverage data for decision support and audit procedures becomes a standard expectation.
ESG Reporting and Sustainability Accounting
Environmental, Social, and Governance reporting has emerged as a significant area requiring CPA expertise. Professionals who understand sustainability reporting frameworks, carbon accounting, and ESG assurance position themselves for growing demand in this space. Major firms are investing heavily in building ESG capabilities.
Technology and Automation Competencies
CPAs must understand how technology transforms their profession, from robotic process automation handling routine tasks to artificial intelligence supporting analysis and decision-making. Those who can evaluate and implement technology solutions, rather than being displaced by them, will thrive as automation reshapes accounting work.
How Do CPA and CA Careers Compare in India?
Indian professionals often evaluate CPA alongside Chartered Accountancy, seeking to understand how these credentials compare for career opportunities in the Indian market. While both designations indicate advanced accounting competence, they offer distinct advantages depending on career goals.
Similarities in Job Functions
CPA and CA credentials prepare professionals for many overlapping roles, particularly in core accounting functions.
Audit and Assurance Overlap
Both CPAs and CAs perform audit and assurance services, examining financial records, testing controls, and providing independent opinions on financial statements. The technical work involved in planning audits, executing procedures, and evaluating evidence is similar across both credentials. Organizations often employ both CPA and CA holders in their audit teams.
Tax Advisory Common Ground
Both credentials enable professionals to provide tax advisory services, though the specific jurisdictions differ. CAs primarily handle Indian taxation, while CPAs specialize in US tax. Many organizations with operations in both countries require both types of expertise, creating complementary demand.
Key Differences in Career Opportunities
Despite overlapping functions, meaningful differences exist in how the credentials position professionals for various opportunities.
Geographic Scope of Practice
The CA credential provides practice rights in India and recognition in several Commonwealth countries, while the CPA enables practice in the United States and is widely recognized internationally. For professionals targeting careers with US-headquartered companies or significant US operations, CPA provides distinct advantages. CA holders seeking to add international credentials often pursue the CPA for this reason.
Industry Preferences and Demand
Multinational corporations with US parent companies, Big 4 firms serving American clients, and organizations requiring US GAAP expertise show a strong preference for CPA holders. Conversely, domestic Indian companies, Indian taxation work, and positions requiring signing authority for Indian statutory audits require a CA qualification. The ideal credential depends on your target employers and career focus.
Salary Comparison in India
Salary comparisons between CPAs and CAs depend heavily on employer type and role. Within Big 4 firms and multinational corporations, CPAs and CAs in similar roles earn comparable compensation. CPAs sometimes command premiums for positions specifically requiring US accounting expertise. Professionals holding both credentials typically earn more than those with either alone, reflecting the value of dual expertise.
Conclusion
Understanding CPA job descriptions helps you make informed decisions about pursuing this credential and positioning yourself for success in the job market. The CPA role encompasses diverse responsibilities from financial statement preparation and audit services to tax planning and strategic advisory, offering multiple career paths aligned with different interests and strengths.
For Indian professionals, the CPA opens doors to roles with Big 4 firms serving global clients, multinational corporations requiring US GAAP expertise, and organizations valuing internationally recognized accounting credentials.
With compensation ranging from ₹6 lakhs at entry level to ₹50 lakhs or more at senior levels, the career opportunities for CPAs continue expanding. Whether you pursue tax, audit, or advisory specialization, the CPA credential positions you for a rewarding career in global finance.
To understand the overall CPA journey, you can also refer to this detailed guide on the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Exam in USA. Or, if you are looking for a detailed guide on how to crack the CPA exam, then read my article on the US CPA exam here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a CPA do on a daily basis?
A CPA’s daily activities depend on their role and specialization. Auditors spend time testing transactions, reviewing documents, and interviewing client personnel. Tax CPAs prepare returns, research tax issues, and advise clients on planning strategies. Advisory CPAs analyze data, develop recommendations, and present findings to stakeholders. All CPAs spend time communicating with colleagues and clients.
Is CPA in demand in India?
Yes, CPA demand in India remains strong and growing. Big 4 firms continue expanding their India operations, multinational corporations are establishing finance centers requiring US GAAP expertise, and Indian companies with international operations increasingly value CPA credentials. The combination of global recognition and specialized US accounting knowledge creates sustained demand.
What is the starting salary for a CPA in India?
Entry-level CPAs in India typically earn between ₹6 lakhs and ₹10 lakhs per annum. Big 4 firms and major multinational corporations offer packages at the higher end of this range, sometimes reaching ₹12 lakhs for exceptional candidates. Starting salaries in tier-one cities like Mumbai and Bangalore tend to exceed those in smaller markets.
Can I work as a CPA in India without US experience?
Yes, many CPAs build successful careers in India without prior US work experience. Indian Big 4 offices, multinational finance centers, and companies with US operations hire CPAs based on their credential and demonstrated competencies. Experience working with US clients or on US GAAP reporting from India is valued but not always required for entry-level positions.
What is the difference between CPA and CA job roles?
While CPAs and CAs perform similar core functions in accounting, audit, and tax, their jurisdictional focus differs. CAs primarily work with Indian accounting standards and tax laws, while CPAs specialize in US GAAP and American taxation. CPAs are particularly valued for roles serving US-headquartered clients, while CAs are essential for Indian statutory requirements.
Which companies in India hire US CPAs?
Major CPA employers in India include Big 4 firms (Deloitte, PwC, EY, KPMG), multinational corporations with Global Capability Centers (Amazon, Google, Microsoft, American Express), IT companies with US operations (Infosys, Wipro, TCS), and Indian companies with international operations. Finance shared services centers also employ significant numbers of CPAs.
Is Big 4 experience necessary for CPA jobs in India?
Big 4 experience is valuable but not strictly necessary for CPA career success in India. While Big 4 provides excellent training, client exposure, and career acceleration, many CPAs build strong careers through corporate finance roles, mid-tier accounting firms, or specialized industry positions. The right path depends on your career goals and preferences.
What skills are most important for CPA job success?
Technical accounting knowledge, analytical thinking, communication skills, and attention to detail are universally important. As careers progress, leadership capabilities, business development skills, and strategic thinking become increasingly valued. Emerging skills in data analytics, technology, and ESG reporting differentiate forward-looking professionals.
Can Indian CPAs work remotely for US companies?
Yes, many Indian CPAs work remotely for US-based companies or clients. This includes employees of multinational corporations’ India centers, Big 4 professionals serving international clients, and independent consultants providing specialized services. Remote work opportunities have expanded significantly, enabling India-based professionals to serve global clients effectively.
How does CPA salary compare to CA salary in India?
CPA and CA salaries in comparable roles at similar employers are generally equivalent. CPAs may command premiums for positions specifically requiring US accounting expertise, while CAs are essential for Indian statutory work. Professionals holding both credentials typically earn more than those with either alone, reflecting the value of dual expertise.
What career level can a CPA reach in India?
CPAs in India can reach the highest levels of finance leadership, including CFO positions at major organizations and partner roles in accounting firms. Career progression depends on performance, business development contribution, and leadership development rather than credential alone. Many successful CFOs and partners at India-based multinational operations hold CPA credentials.
Is CPA worth it for Indian professionals already working in finance?
For finance professionals targeting careers with multinational corporations, Big 4 firms, or organizations requiring US GAAP expertise, CPA adds significant value. The credential differentiates candidates, opens doors to specialized roles, and typically commands compensation premiums. Working professionals can complete CPA while employed through structured study programs.
How long does it take to get a CPA job after passing the exam?
Most candidates who pass their CPA exams and actively job search find positions within three to six months. Those with relevant experience or existing employer relationships often transition faster. Job search success depends on factors including location flexibility, salary expectations, specialization alignment with market demand, and interview skills.
What industries pay the highest salaries to CPAs in India?
Financial services, technology, and consulting typically offer the highest CPA compensation in India. Big 4 advisory practices and multinational corporations’ finance leadership roles also pay premium salaries. Specialized roles in areas like transaction advisory, forensic accounting, and international taxation often command above-market compensation.
Can I pursue CPA while working full-time in India?
Yes, many Indian professionals complete CPA while working full-time. The exam requires approximately 300 to 400 hours of study, typically spread over 12 to 18 months. SkillArbitrage offers a CPA Prep and Global Finance Career Acceleration Program designed for working professionals, with structured study schedules accommodating employment demands. Success requires consistent study habits and effective time management.






 Allow notifications
Allow notifications